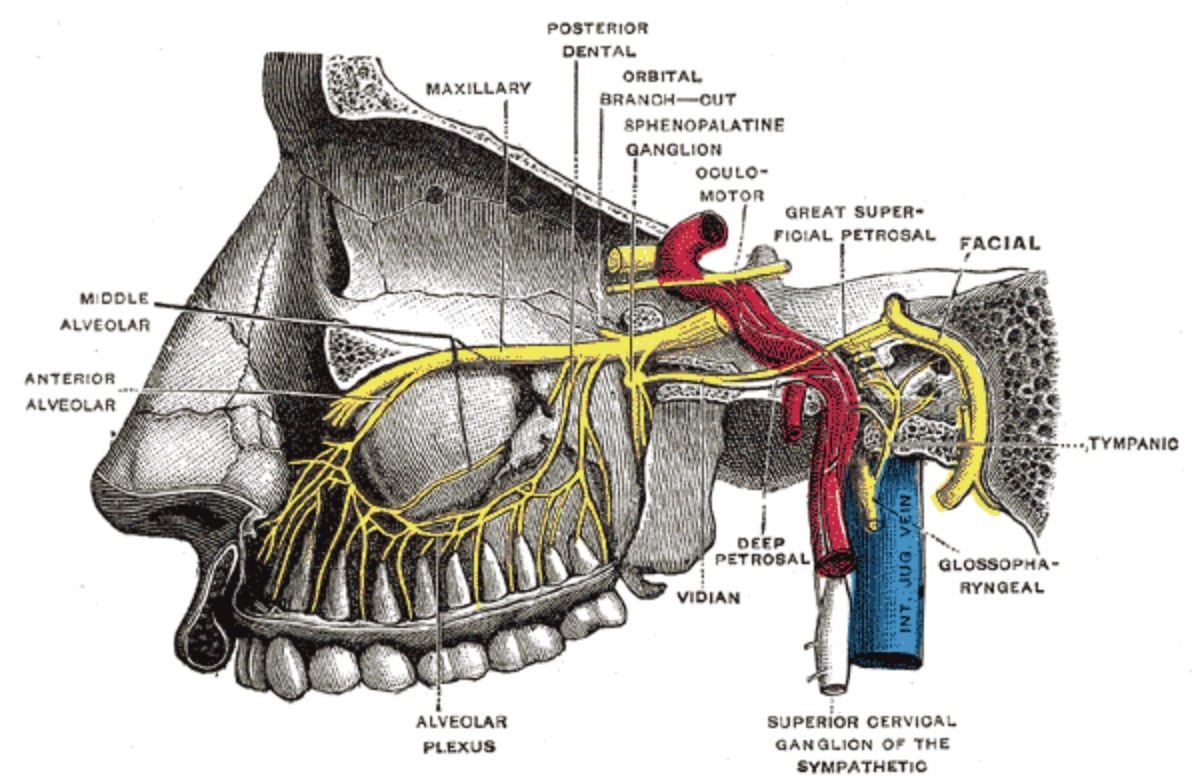
Overview
Targeted blocking of the sphenopalatine ganglion (SPG) is becoming more popular as an alternative to opioids for treating headaches, migraines, and other pain and neuralgias, although the literature is still mixed.1-5
It’s not completely understood why SPG blocking is effective